In recent years, laser technology has revolutionized the way metals are cut and processed, offering faster, more accurate, and cost-effective methods compared to traditional cutting techniques. Laser for metal cutting has become a go-to solution for industries requiring high precision, speed, and the ability to work with a variety of metal types. From aerospace to automotive manufacturing, lasers have proven to be a game-changer in metalworking, providing unmatched cutting capabilities.
This article will delve into how laser cutting technology works for metal, the different types of lasers used, and the industries that benefit most from this advanced process.
At its core, laser cutting involves directing a high-powered laser beam onto a metal surface to melt, vaporize, or blow away the material. The result is a clean, precise cut with smooth edges. Laser cutting is preferred for its ability to handle a wide range of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, and titanium, with high accuracy.
The technology typically uses a CO2 laser, a fiber laser, or a disk laser depending on the specific requirements of the cutting process, such as the material, thickness, and precision level required.
When choosing a laser for metal cutting, it’s essential to understand the different types of lasers available. Each type comes with its own set of characteristics, making it better suited to particular applications. The three most common types of lasers for metal cutting are:
CO2 lasers are one of the oldest and most widely used laser technologies for cutting metal. These lasers use carbon dioxide as a medium to generate the laser beam. The beam is typically delivered through a system of mirrors or fiber optics to focus on the material to be cut. CO2 lasers are known for their versatility and ability to cut a wide variety of metals, especially thicker materials like steel.
Best For: Cutting thick metals, low to medium-speed applications, and diverse material types.


Fiber laser cutting machines use fiber-optic cables as a medium to generate the laser beam. This type of laser offers a more concentrated beam and is more efficient compared to CO2 lasers, allowing for faster cutting speeds and less power consumption. Fiber lasers are highly precise and particularly effective at cutting thin to medium-thickness materials with excellent edge quality.
Best For: Precision cutting of thin metals, high-speed applications, and energy-efficient operations.
Disk lasers use a thin disk of solid-state material to generate the laser beam. These lasers combine the high efficiency of fiber lasers with the power of CO2 lasers, offering excellent cutting capabilities for various metals. Disk lasers can handle thicker materials while maintaining precision.
Best For: Heavy-duty cutting and applications requiring a balance of speed, precision, and power.

Laser cutting has become increasingly popular in industries around the world due to its impressive benefits. Let’s look at the primary advantages of using laser for metal cutting:
Laser cutting machines provide an unparalleled level of precision, capable of creating intricate designs with tight tolerances. The focused laser beam allows for clean, sharp edges with minimal distortion. This level of precision is difficult to achieve with traditional mechanical cutting methods.
Example: Producing intricate components like automotive brackets or electronic housings.
Laser cutting is one of the fastest metal cutting techniques available. The high-powered lasers cut through metal quickly, reducing production time and increasing efficiency. This speed is especially valuable in high-volume manufacturing environments where time is critical.
Example: Mass production of sheet metal parts for the automotive industry.
Laser cutting produces highly accurate cuts, meaning there is less material waste compared to traditional cutting methods. The precision of the laser ensures that the material is used efficiently, making it a cost-effective option in the long run.
Example: Cutting large metal sheets with minimal scrap material.
Laser cutting machines can handle a wide variety of metals, including high-performance alloys, and can even cut non-metals like plastics and wood. This versatility makes laser cutting an ideal solution for businesses working with multiple materials or those requiring custom parts.
Example: Cutting stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel for diverse applications in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Laser cutting machines, particularly fiber lasers, have fewer moving parts compared to traditional mechanical cutting equipment. This results in lower maintenance costs and less wear and tear. The durable nature of laser machines contributes to a longer lifespan and fewer breakdowns, improving overall productivity.
Example: High-volume manufacturing environments that benefit from reduced downtime.
Laser cutting is widely used in various industries due to its precision and ability to handle complex, intricate designs. Some of the primary sectors that benefit from laser for metal cutting include:
The automotive sector requires high-precision metal cutting to produce various components, from chassis parts to engine components. Laser cutting ensures the accurate, fast production of parts, which is crucial in a high-volume industry.
Example: Cutting automotive body panels, engine parts, and exhaust systems.

The aerospace industry demands high-precision metal cutting for parts that must meet stringent safety standards. Laser for metal cutting offers the ability to produce lightweight, complex components that are both accurate and reliable.
Example: Cutting aircraft structural components, turbine blades, and engine casings.
The electronics industry uses laser cutting for precise, small-scale components. Laser cutting is ideal for creating delicate, intricate designs, such as circuit boards and connectors, with high accuracy.
Example: Manufacturing circuit boards, electronic enclosures, and heat sinks.
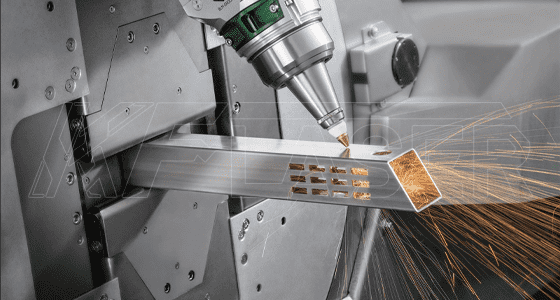
Laser cutting is a core technology in metal fabrication, where it is used for creating custom parts, prototypes, and final products. The high accuracy and minimal post-processing required make it an essential tool for fabricators.
Example: Cutting custom metal brackets, signage, and decorative panels.
Laser cutting is also heavily used in the medical device industry, where high precision is a necessity for creating small, complex parts like surgical instruments or medical implants.
Example: Cutting surgical tools, stents, and medical prosthetics.
When selecting a laser for metal cutting, several key factors need to be considered to ensure you choose the right technology for your specific needs. These factors include:
Laser cutting continues to be a fundamental part of the manufacturing process, and with new advancements in technology, its use will only expand across more industries. Whether you are involved in metal fabrication, automotive, or electronics, understanding how to leverage laser for metal cutting will give your business the competitive edge in precision, speed, and efficiency.