In the fast-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, laser metal cutting equipment stands out as one of the most powerful and versatile tools available. This cutting-edge technology has revolutionized the way industries cut, shape, and process metals. From creating intricate designs to handling large-scale production runs, laser metal cutting equipment offers unparalleled precision, speed, and efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the various types of laser cutting systems, their advantages, and how they are transforming industries across the globe.
Laser metal cutting refers to a process where a focused laser beam is used to cut or engrave metals with extreme precision. The laser beam melts or vaporizes the material along the cutting path, allowing for smooth, sharp edges and minimal material waste.
The equipment used for laser cutting typically consists of a laser source (CO2, fiber, or YAG lasers), optics to focus the beam, a cutting head, and a CNC (computer numerical control) system that controls the movement of the laser. With the ability to handle various metal types and thicknesses, laser cutting equipment has become essential in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace, manufacturing, and beyond.
Laser cutting offers several advantages over traditional methods such as plasma or mechanical cutting. Below are some reasons why more industries are turning to laser technology for metal cutting.
One of the main reasons manufacturers prefer laser cutting is its ability to produce extremely precise cuts. The laser beam can be adjusted to a very fine diameter, allowing for tight tolerances and intricate designs. This precision makes it ideal for applications where detail and accuracy are crucial, such as in the aerospace and electronics industries.
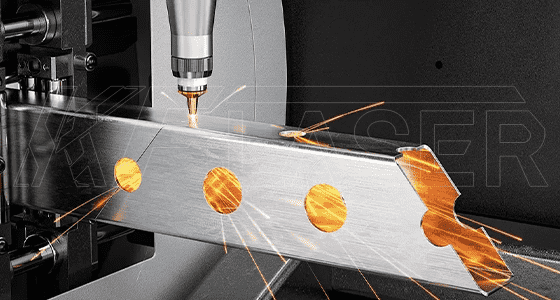

Laser cutting provides clean, smooth edges with minimal burrs or distortion, making it especially beneficial for high-quality metalwork. The minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ) reduces the risk of material distortion or oxidation, which can be a problem with traditional cutting methods.
Another significant advantage of laser cutting is its speed. The process is highly efficient, reducing the time required to cut and process metals. Laser cutters can work continuously without the need for tool changes, unlike mechanical cutting methods that require frequent adjustments. This speed makes laser cutting ideal for both small and large production runs.

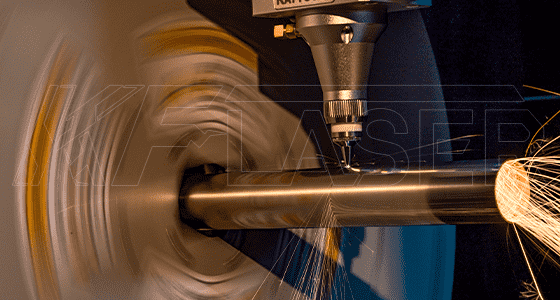
Laser cutting is a material-efficient process. The precision of the cuts ensures minimal waste, which helps manufacturers reduce costs and minimize their environmental impact. This is particularly advantageous when working with expensive metals such as stainless steel, titanium, and aluminum.
Laser cutting equipment can be used to cut various metals, including steel, aluminum, stainless steel, copper, brass, and titanium. It can also process materials of varying thicknesses, making it suitable for a wide range of industries and applications.

When choosing a laser metal cutting machine, it’s important to understand the different types of lasers available. The type of laser cutting equipment used depends on the specific material and thickness requirements, as well as the desired cutting quality.
1. CO2 Laser Cutting Machines
CO2 lasers are one of the most widely used types of laser cutting systems, particularly in industries requiring precise cuts on non-ferrous metals. These systems use carbon dioxide gas as the laser medium and are highly effective for cutting materials like steel, aluminum, and brass. While CO2 lasers are highly accurate, they are generally slower than fiber lasers when cutting thin metals.
2. Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Fiber lasers are known for their superior efficiency, especially when cutting thin to medium thickness metals. These machines use a fiber optic cable to deliver the laser beam, which allows for higher power density and faster cutting speeds. Fiber lasers are ideal for cutting metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. They also offer lower operating costs and greater energy efficiency compared to CO2 lasers.
3. YAG Laser Cutting Machines
YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser systems use a solid-state laser to cut metals and are especially effective for thicker materials. While not as common as CO2 and fiber lasers, YAG lasers are still used in applications that require deep penetration and high power.
4. Multifunctional Laser Machines
Some modern laser cutting systems can perform multiple tasks beyond just cutting, such as engraving and marking. These multifunctional machines are versatile and can be customized for various industries, including automotive, electronics, and sign-making.
Laser cutting is used in a wide variety of industries, each benefiting from the equipment’s precision, speed, and versatility.
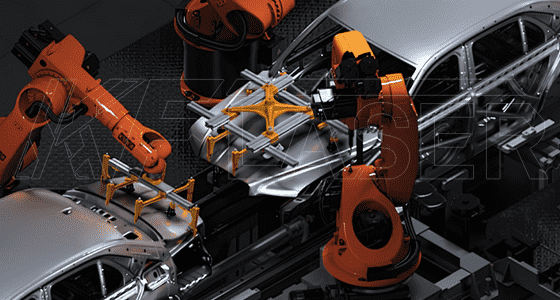
In the automotive sector, laser cutting plays a vital role in producing high-quality parts and components. From engine parts to chassis and body panels, laser cutting ensures that each part is manufactured with precision, meeting the strict tolerances required for vehicle safety and performance.

In aerospace, laser cutting is used to create components such as turbine blades, structural components, and airframes. The need for lightweight yet strong parts means that laser cutting is essential for producing materials that meet the high standards of strength and accuracy.
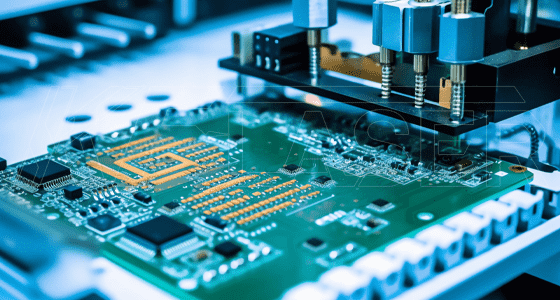
Laser cutting is frequently employed in the electronics industry to cut intricate patterns and designs in printed circuit boards (PCBs). The precision and speed of laser cutting ensure that electronic components are manufactured accurately and efficiently.
In the world of signage, custom laser-cut metal panels and logos are used to create eye-catching designs. Additionally, the architectural industry utilizes laser cutting for decorative panels, facades, and structural elements, where both functionality and aesthetic appeal are critical.
The medical industry relies on laser cutting for the production of surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. Precision is paramount in these applications, and laser cutting ensures the production of parts that meet strict standards for safety and performance.
Selecting the right laser metal cutting equipment can be a daunting task, as various factors influence the choice of machine. Here are some important considerations:
Different types of lasers are suited to different materials. For instance, fiber lasers are ideal for cutting thinner metals, while CO2 lasers are more effective for thicker materials. Always consider the material type and the thickness of the metal you plan to cut before selecting the appropriate laser.
Cutting speed varies depending on the laser type, material thickness, and laser power. If high-speed cutting is a priority for your application, fiber lasers tend to offer faster cutting speeds compared to CO2 lasers.
While laser cutting systems are highly efficient, they do require regular maintenance and energy consumption. Fiber lasers tend to have lower operating costs than CO2 lasers, but it’s essential to calculate the long-term costs of operating the system, including energy, maintenance, and consumables.
Consider the level of precision needed for your project. Laser cutting equipment can achieve tolerances down to a few micrometers, making it suitable for applications that require extremely tight tolerances and fine details.
Some laser cutting systems offer additional features, such as automatic loading and unloading, advanced software for design and programming, and multi-axis capabilities for more complex cuts. These features can increase productivity and ease of use, so consider your specific needs before investing in equipment.
The use of laser metal cutting equipment continues to grow as technology advances, with innovations leading to faster, more efficient systems. As manufacturers seek to increase productivity while reducing costs, laser cutting offers a versatile solution that combines high quality, speed, and minimal material waste.

From small workshops to large industrial plants, laser cutting is transforming the way metal parts are made. By providing consistent precision, a cleaner cut, and greater flexibility, it has become an essential tool for businesses striving to meet the demands of modern manufacturing.