Notícias
Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to Metal Cutting Methods
When it comes to cutting metal, industries worldwide rely on various technologies to achieve precision, velocidade, and cost-efficiency. Among the most common methods are laser cutting vs plasma cutting, each offering distinct advantages and limitations depending on the application. While both processes have earned their place in the fabrication world, understanding the key differences can help manufacturers make informed decisions based on their specific needs. Whether you’re working with stainless steel, alumínio, or mild steel, the method you choose can impact everything from production cost to product quality.

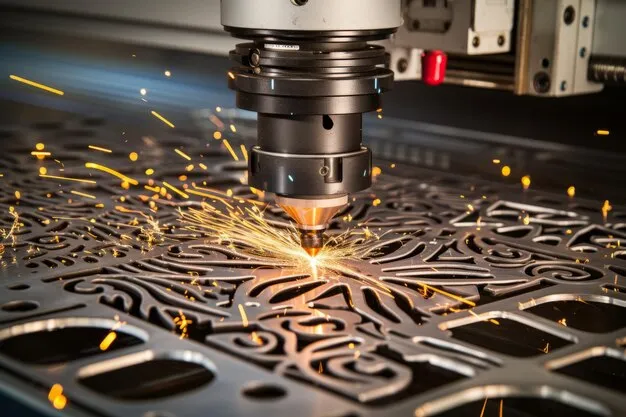
Ⅰ. What is Corte a laser?
◆ The Basics of Laser Cutting Technology
Laser cutting is a process that uses a focused laser beam to cut through metal, plástico, or other materials. O feixe de laser derrete, queimaduras, ou vaporiza o material, leaving behind a precise cut. The laser’s heat is extremely focused, which allows for clean, sharp edges with minimal heat-affected zones.
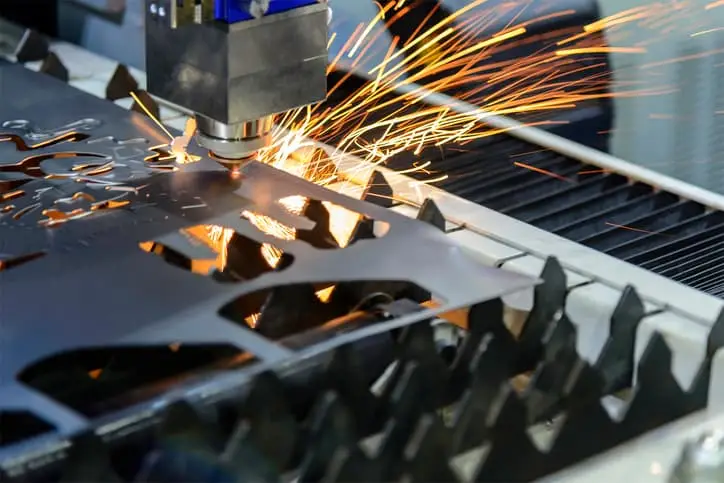

★ Precision:
Laser cutting is known for its superior accuracy, making it ideal for intricate and detailed designs. The precision of laser cutting ensures that the edges are smooth and require little to no post-processing.
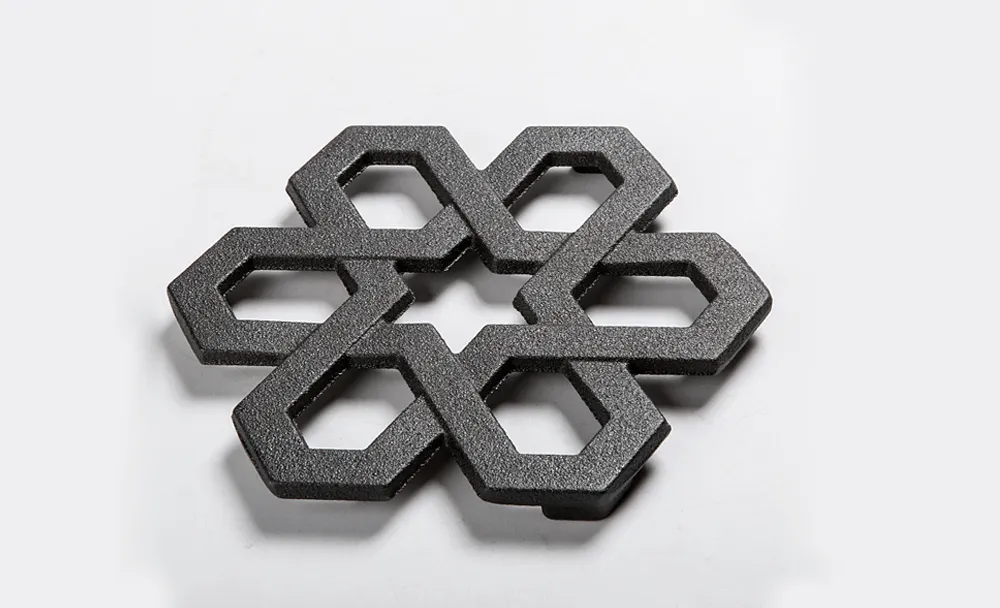

★ Speed:
Laser cutting can be faster than other methods, especially when cutting thinner sheets of metal, increasing production efficiency.
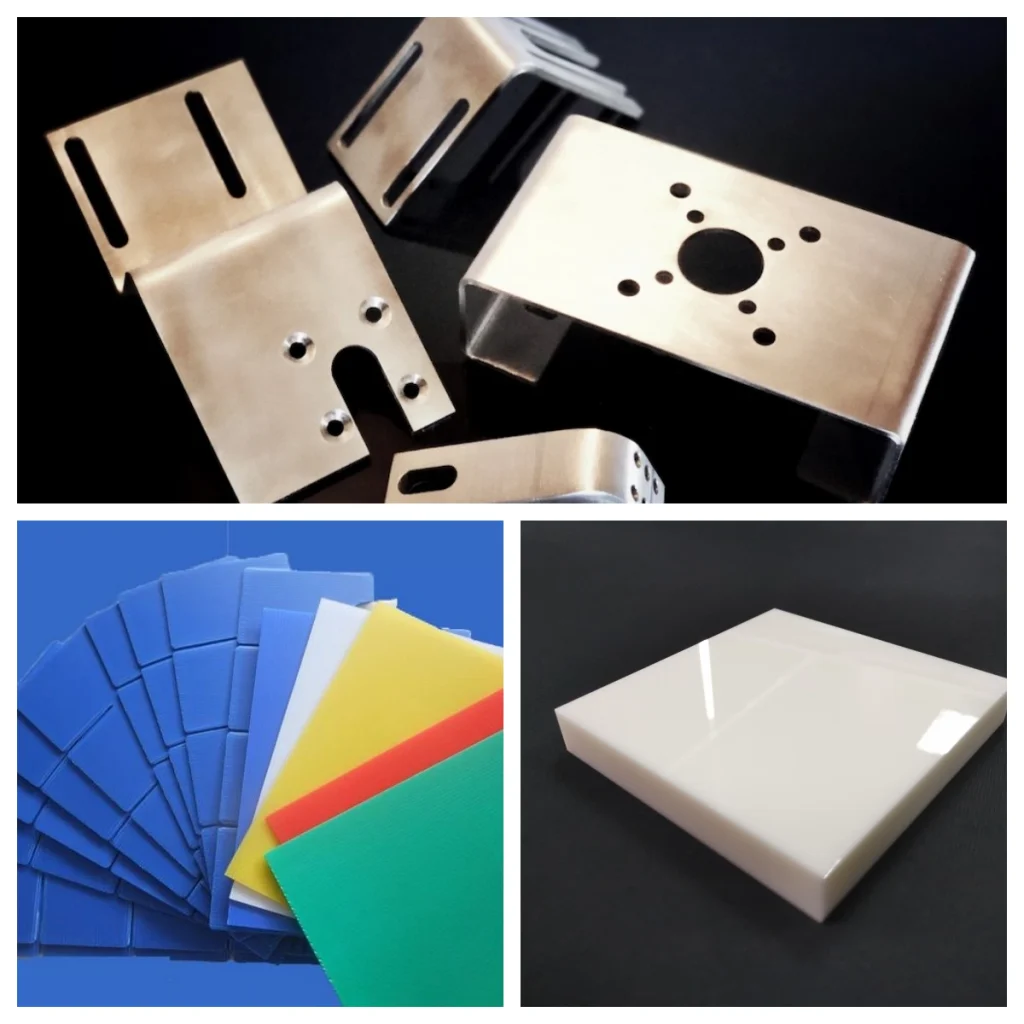
★ Versatility:
It can cut a variety of materials, incluindo metais, plásticos, e cerâmica. Além disso, laser cutters can handle both thin and thick materials.

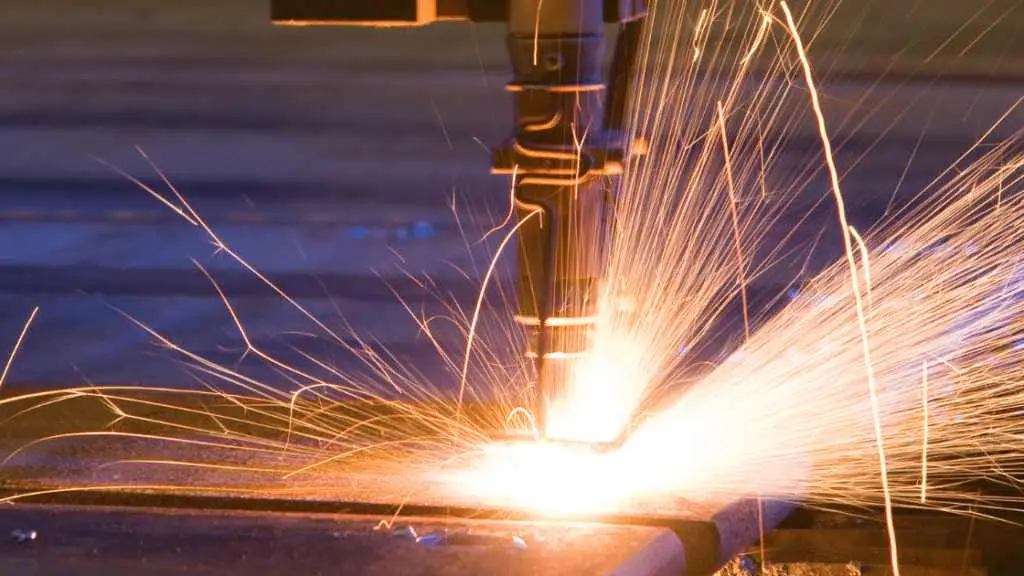
Ⅱ. What is Plasma Cutting?
◆ The Plasma Cutting Process
Plasma cutting uses an ionized stream of gas to cut through metal. The gas, which is electrically conductive, is turned into plasma and directed onto the metal. The plasma stream heats the metal to the point where it melts and is blown away, criando um corte.

◆ Advantages of Plasma Cutting
★ Cost-Effective: Plasma cutting systems are generally less expensive than laser cutting systems, especially for thicker materials, making it a more budget-friendly choice.
★ Versatility for Thick Materials: Plasma cutters are highly efficient at cutting thicker metals (up to several inches), unlike lasers that may struggle with thicker sheets.
★ Speed for Rough Cuts: Plasma cutting is faster for less intricate cuts in thick materials, making it suitable for large production runs.
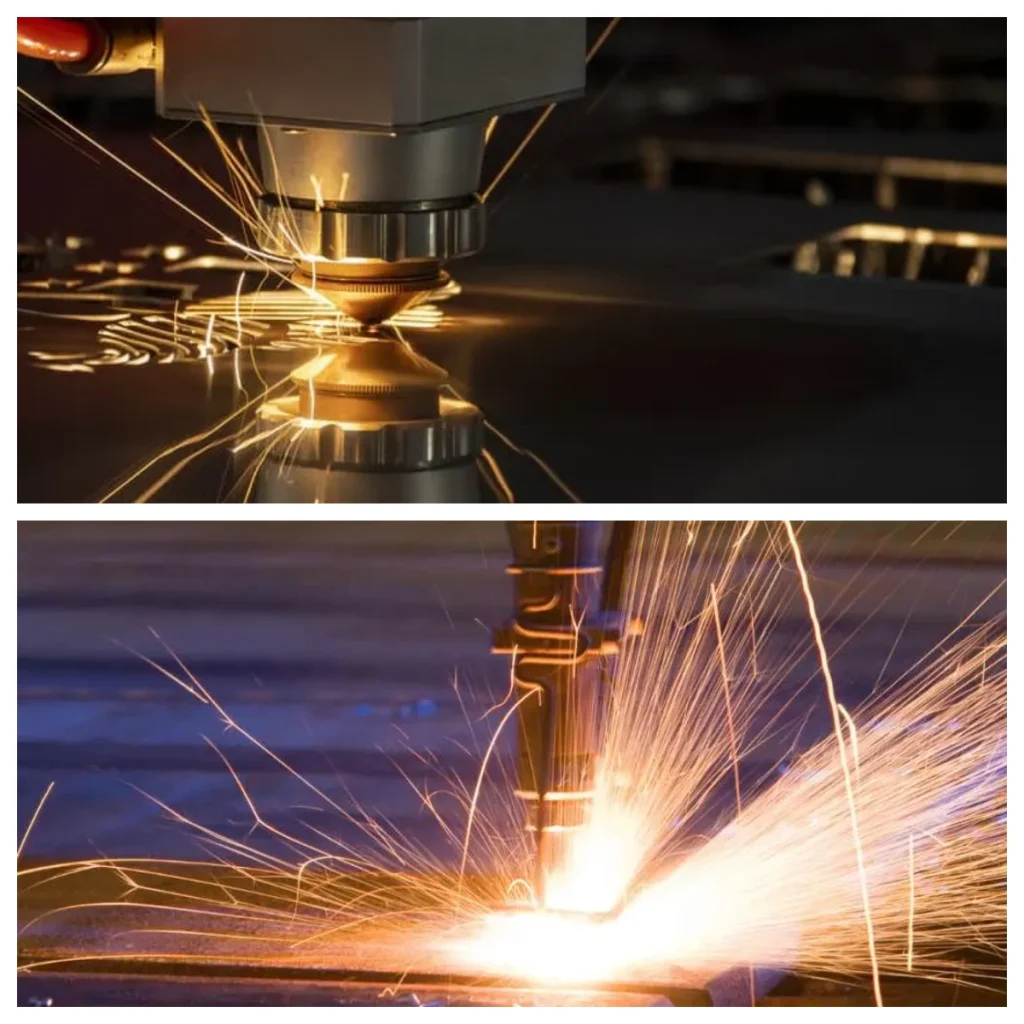
Ⅲ. Key Differences Between Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting
◆ Cutting Precision
One of the most significant differences between laser cutting vs plasma cutting is the level of precision. Laser cutting excels at making intricate, detailed cuts with tight tolerances. This makes it the preferred choice for industries requiring high precision, such as aerospace or automotive. Plasma cutting, por outro lado, offers less precision, and its cuts tend to be rougher. No entanto, it is still suitable for many general metalworking applications where the speed of cutting is more important than the quality of the edges.

◆ Material Thickness and Types
Laser cutting machines can handle thin materials very efficiently, cutting with incredible accuracy. No entanto, when it comes to cutting thicker metals, plasma cutting becomes more efficient. Plasma cutting systems can easily cut through metals of greater thickness (often up to 2 inches or more), making it a better choice for heavy-duty applications. Laser cutters, while capable of cutting thick materials, may require more time and higher power.
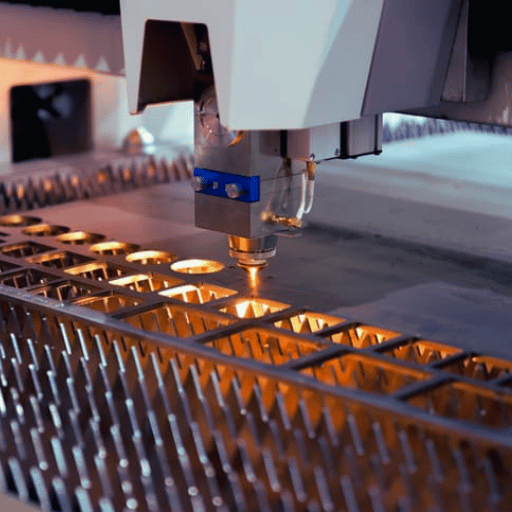

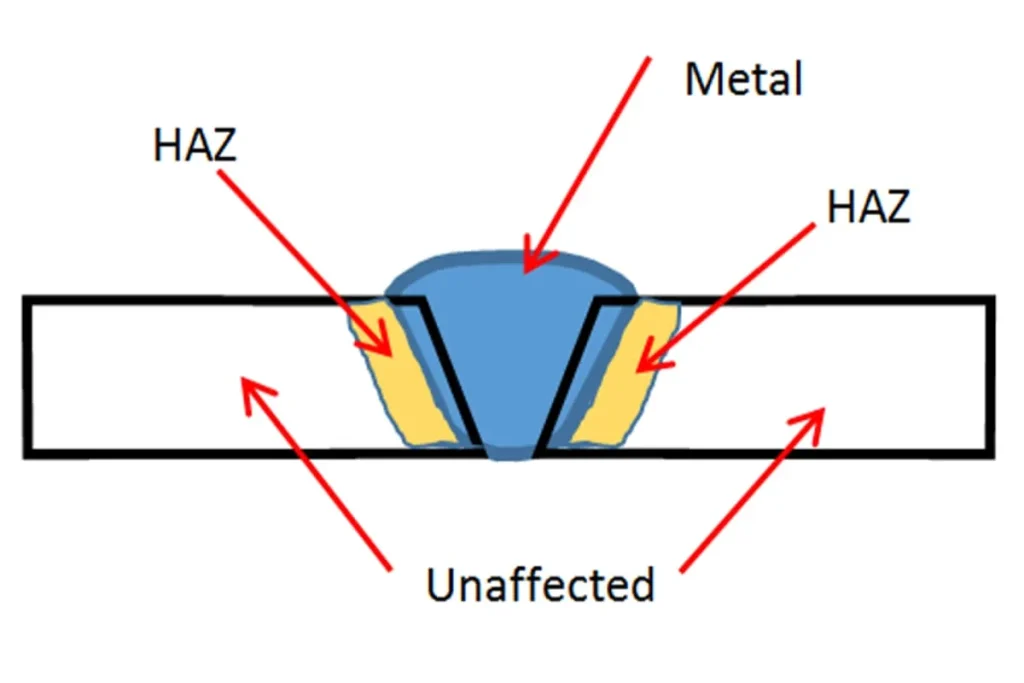
◆ Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
The heat-affected zone is another critical factor when comparing laser cutting vs plasma cutting. Laser cutting generates a smaller HAZ, meaning there is less distortion in the material around the cut. This makes laser cutting a better option for materials that are sensitive to heat distortion. Plasma cutting, no entanto, creates a larger HAZ, which can lead to warping or bending of the metal, especially in thinner sheets.
◆ Operational Costs
While plasma cutting systems are generally more affordable to purchase than laser cutting machines, the operational costs can vary depending on the material being cut. Plasma cutting uses consumables such as electrodes, nozzles, and gases, which need to be replaced regularly. Laser cutting systems, por outro lado, typically have fewer consumables and maintain their efficiency for longer periods. No entanto, the initial investment in a laser cutting machine can be higher.
4. When to Use Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting
◆ Laser Cutting Applications
Laser cutting is ideal when high precision is required, and the material being cut is relatively thin. Industries such as electronics, Automotivo, and medical device manufacturing benefit greatly from the ability to produce complex shapes with minimal material waste. Applications include:
★ Fine engraving and etching
★ Intricate designs and patterns
★ Thin metal sheet cutting

◆ Laser Cutting Applications
Laser cutting is ideal when high precision is required, and the material being cut is relatively thin. Industries such as electronics, Automotivo, and medical device manufacturing benefit greatly from the ability to produce complex shapes with minimal material waste. Applications include:
★ Fine engraving and etching
★ Intricate designs and patterns
★ Thin metal sheet cutting
◆ Plasma Cutting Applications
Plasma cutting is better suited for larger, less intricate cuts in thicker materials. It’s widely used in construction, construção naval, and automotive manufacturing, where speed is a priority, and the cut quality is not as critical. Applications include:
★ Cutting thicker metal sheets (até 2 inches)
★ Heavy-duty industrial applications
★ General-purpose metal cutting
Ⅴ. Cost Comparison of Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting
◆ Initial Investment
Como mencionado anteriormente, the initial investment in a laser cutting machine tends to be higher than that of a plasma cutting machine. The price of a laser cutting machine can range from several thousand dollars to over $100,000 depending on the size and power, whereas plasma cutting systems can be found at a significantly lower price point.

◆ Operational Costs
For laser cutting vs plasma cutting in terms of operational costs, laser cutting systems tend to be more energy-efficient for thin material cutting, but plasma systems are more cost-effective for heavy-duty applications involving thick materials. The cost of consumables and maintenance also plays a role in overall costs.
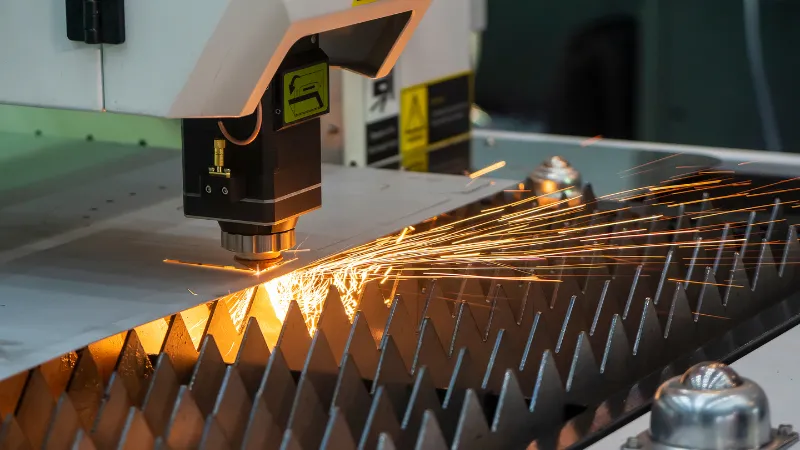

Ⅵ. Which Cutting Method Is Right for You?
Choosing between laser cutting vs plasma cutting depends on several factors including the type of material, a espessura do material, precision requirements, and budget constraints. If your project demands high precision, desenhos intrincados, and thinner materials, laser cutting is the best option. For those looking for a cost-effective method that can handle thicker materials at a faster speed, plasma cutting may be the preferred choice.
Em última análise, both cutting methods have their strengths and applications, and knowing when and where to use each can make all the difference in optimizing production efficiency and quality. Whether you’re working on a custom project or large-scale production, understanding laser cutting vs plasma cutting will help you make the most informed decision for your business.
Notícias principais
-
 Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machine For Sale05 Dec 2025
Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machine For Sale05 Dec 2025 -
 4000 Watt Laser | Industrial Cutting Power02 Dec 2025
4000 Watt Laser | Industrial Cutting Power02 Dec 2025 -
 6 corte a laser kw | Guia de precisão industrial28 novembro 2025
6 corte a laser kw | Guia de precisão industrial28 novembro 2025 -
 Revolucionando a indústria com máquina de corte a laser para tubos de aço25 novembro 2025
Revolucionando a indústria com máquina de corte a laser para tubos de aço25 novembro 2025 -
 10Corte a laser kW | Precisão & Poder21 novembro 2025
10Corte a laser kW | Precisão & Poder21 novembro 2025
Categorias de produtos
- Cortador a laser de metal
- Máquina de solda a laser
- Máquina de limpeza a laser
- Máquina marcadora a laser
- Máquina de freio de imprensa




