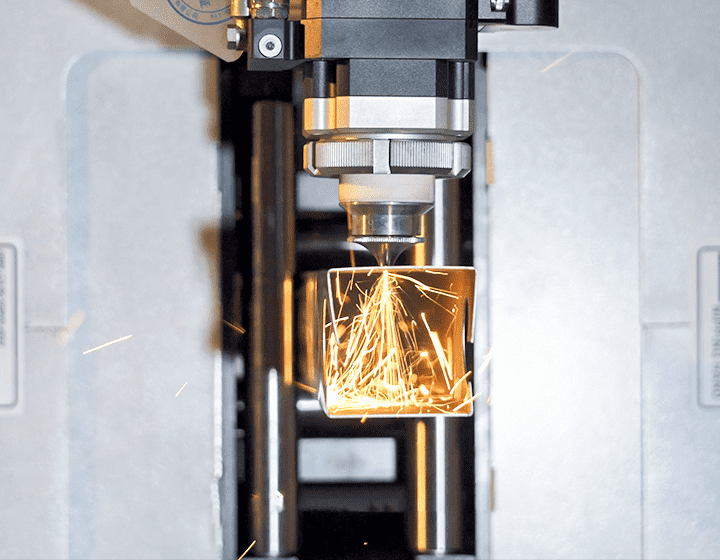
News
Types of Laser Cutting Machines: Understanding the Technology Behind Precision
In the world of modern manufacturing, types of laser cutting machines have become essential tools for achieving high precision and efficiency. Whether it’s for industrial, aerospace, or medical applications, laser cutting technology has revolutionized the way we cut and shape materials. But with so many different laser cutting machines available, how do you know which one is right for your specific needs?

Laser cutting involves using a focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material to create precise cuts or holes. The laser cutting process has several advantages, such as high accuracy, clean cuts, minimal waste, and the ability to cut complex shapes. However, choosing the right type of laser cutting machine can be a challenging task, especially with the wide range of options available.

In this article, we will explore the various types of laser cutting machines, their unique features, and how to choose the most suitable one for your application.
Key Types of Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutting machines come in different configurations based on the type of laser source, the materials they are designed to cut, and their intended use in various industries. Let’s take a closer look at the main types of laser cutting machines:
1. CO2 Laser Cutting Machines
CO2 lasers are one of the most widely used types of lasers in the cutting industry. These lasers emit light in the infrared spectrum, which is absorbed by many materials, making them highly efficient for cutting a wide variety of materials.
Key Features:
CO2 lasers are ideal for cutting non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, and plastics, but they can also be used for metals like stainless steel and aluminum.They offer excellent precision, especially for thin to medium thickness materials.CO2 lasers are known for their ability to produce smooth, clean cuts with minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ).

Applications:
- Woodworking: CO2 lasers are often used to cut wood for furniture and cabinetry.
- Acrylic Fabrication: Perfect for cutting intricate designs in acrylic sheets for signs and displays.
- Metals: Used for cutting thin sheets of metals, especially in industries like automotive and signage.

2. Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Fiber lasers have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their high energy efficiency and ability to cut through a wide range of materials with superior speed and precision. Unlike CO2 lasers, fiber lasers generate laser light through a fiber optic cable.
Key Features:
Fiber lasers are more efficient in terms of power consumption than CO2 lasers, making them ideal for high-volume cutting applications.They can cut through metals such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and even reflective materials like brass and copper.Fiber lasers provide extremely fine focal points, which results in highly detailed and clean cuts.

Applications:
- Metal Fabrication: Ideal for industries that require high-speed, high-precision cutting of metal components, such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
- Signage and Engraving: Perfect for cutting intricate shapes and designs in metal sheets.
- Thin Metal Cutting: Fiber lasers excel at cutting thin metal sheets with excellent speed and precision.

3. Crystal Laser Cutting Machines (Nd:YAG)
Crystal laser cutting machines use a solid-state laser technology that generates light through a crystal medium, typically neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG). These lasers are often used for specific applications in industries where high-power cutting is needed.
Key Features:
Nd:YAG lasers provide a highly focused laser beam, allowing for extremely precise cutting.These machines are capable of cutting a variety of materials, including metals and ceramics.Crystal lasers can be used for both cutting and welding, making them versatile for multiple manufacturing processes.
Applications:
- Metalworking: Suitable for cutting thicker metals with high precision.
- Medical Equipment: Used in applications where precision is critical, such as medical devices and implants.
- Ceramics and Glass: Crystal lasers can be used for cutting brittle materials like glass and ceramics.
4. Diode Laser Cutting Machines
Diode lasers are relatively newer compared to CO2 and fiber lasers, but they offer unique advantages. These lasers use semiconductor diodes as their source of laser light, which makes them compact and energy-efficient.
Key Features:
Diode lasers are often used for micro-cutting applications due to their precision.They are especially effective in applications that involve thin materials and require minimal heat input.These lasers are highly versatile and can be used for both metal and non-metal cutting, with applications in areas like electronics and medical device manufacturing.
Applications:
- Electronics Manufacturing: Diode lasers are often used in the cutting and engraving of small parts and components in the electronics industry.


- Precision Parts: Ideal for micro-cutting applications that require extreme precision, such as in medical device manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Laser Cutting Machine for Your Needs
Now that we’ve explored the different types of laser cutting machines, how do you choose the right one for your specific needs? Here are some factors to consider:
- Material Type: Determine what materials you need to cut. For instance, if you’re cutting metals, a fiber laser may be the best choice. If you’re cutting wood or acrylic, a CO2 laser could be more appropriate.
- Cutting Thickness: Consider the thickness of the materials you’ll be working with. Fiber lasers excel at cutting thin to medium thickness metals, while CO2 lasers are better suited for thin materials.
- Precision and Speed: Depending on your production requirements, you may prioritize precision or cutting speed. Fiber lasers tend to offer faster cutting speeds, while CO2 lasers provide smoother finishes.


- Budget and Energy Efficiency: Fiber lasers are typically more energy-efficient, which can help reduce operational costs. However, they might come at a higher initial investment than CO2 lasers. Assess your budget and operational needs carefully.
- Maintenance and Durability: Consider the long-term maintenance and durability of the laser cutting machine. Fiber lasers, for example, typically require less maintenance than CO2 lasers due to fewer moving parts.

Conclusion
Laser cutting technology continues to evolve, offering a range of machines that cater to diverse industrial needs. By understanding the different types of laser cutting machines, their unique features, and their applications, manufacturers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity, precision, and cost-effectiveness. Whether it’s CO2, fiber, crystal, or diode lasers, choosing the right machine is crucial for achieving the best results in your cutting processes.
Top Stories
-
 Unleashing the Power of Tube Laser Cutting Machines: A Comprehensive Guide07 Mar 2026
Unleashing the Power of Tube Laser Cutting Machines: A Comprehensive Guide07 Mar 2026 -
 How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter for Sale: A Buyer’s Complete Guide03 Mar 2026
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter for Sale: A Buyer’s Complete Guide03 Mar 2026 -
 CNC Laser for Metal | Precision Cutting28 Feb 2026
CNC Laser for Metal | Precision Cutting28 Feb 2026 -
 CNC Laser Tube Cutting Machine | Precision Machines for Sale24 Feb 2026
CNC Laser Tube Cutting Machine | Precision Machines for Sale24 Feb 2026 -
 4KW Fiber Laser Cutting Machine | Industrial Guide20 Feb 2026
4KW Fiber Laser Cutting Machine | Industrial Guide20 Feb 2026
Product Categories
- Metal Laser Cutter
- Laser Welder Machine
- Laser Cleaner Machine
- Laser Marker Machine
- Press Brake Machine