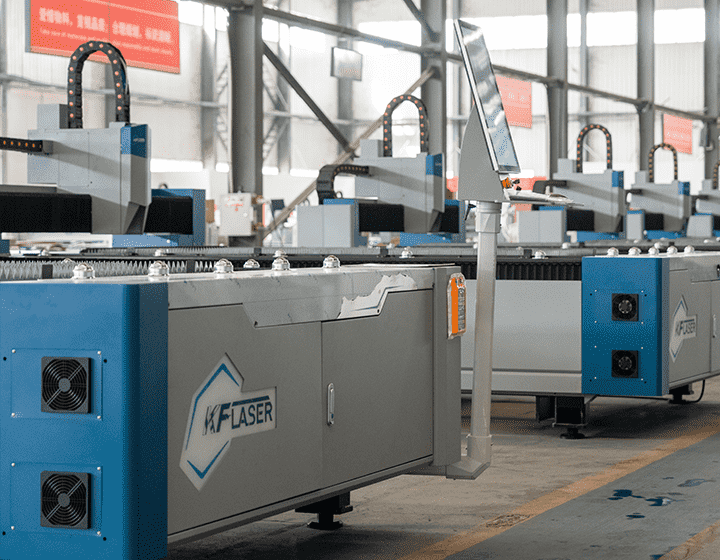
News
An In-Depth Guide to Laser Cutting Machinery: Efficiency, Precision, and Innovation
1. Understanding Laser Cutting Machinery: Precision Meets Productivity
Laser cutting machinery has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, speed, and versatility. From automotive to aerospace, these machines are integral in producing intricate parts and structures, enhancing production capabilities across various sectors. This guide will explore the core principles of laser cutting machinery, delve into its numerous benefits, and discuss the various types and applications to help manufacturers make informed decisions.

Whether you are new to the technology or looking to optimize your production line, understanding the intricacies of laser cutting machinery is essential for achieving the best results.
For more information, please click https://kf-laser.com/
2. How Does Laser Cutting Machinery Work?
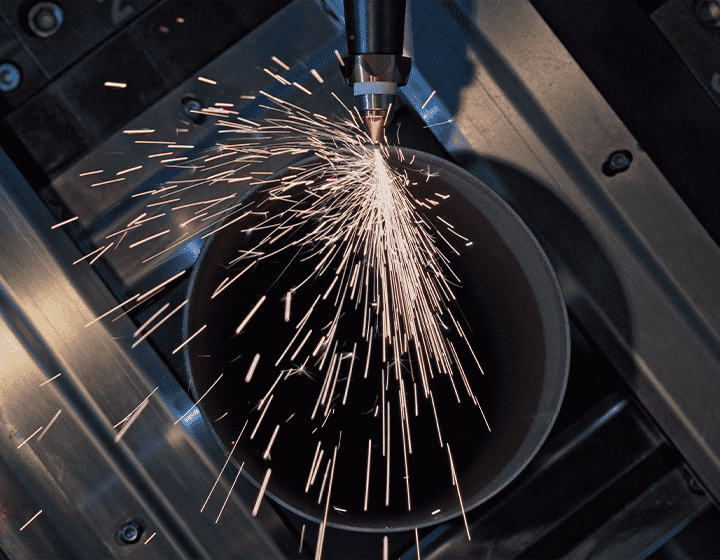
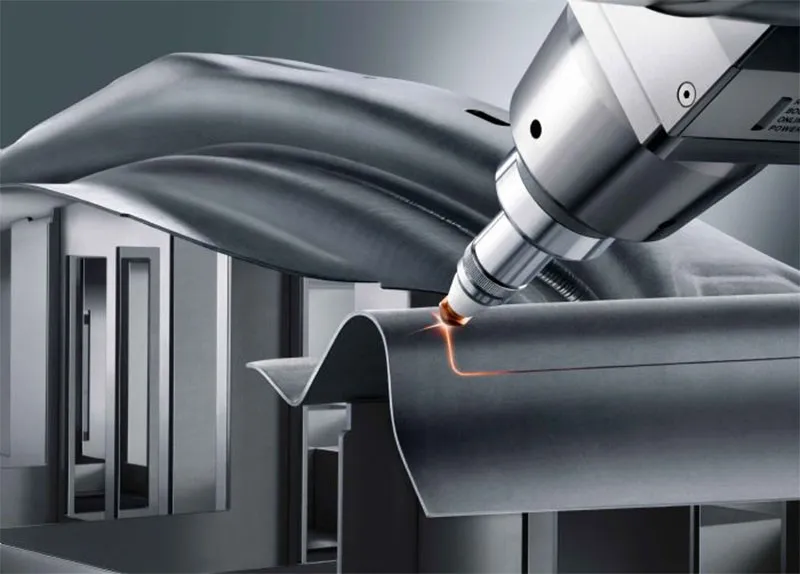
Laser cutting machinery uses a highly concentrated laser beam to melt, vaporize, or burn through materials, enabling intricate cuts with precision. This process relies on advanced optics and CNC (computer numerical control) systems to guide the laser across the material, ensuring repeatability and accuracy.
The video below is a demonstration of KF laser 6000W cutting 16mm carbon steel.
- Key Components of Laser Cutting Machinery
– Laser Source: This is the powerhouse of the machine, where the laser beam is generated. Fiber lasers and CO2 lasers are the most common types used in metal cutting.
– Cutting Head: The cutting head houses lenses that focus the laser beam onto the workpiece. It directs the energy to a pinpoint spot, enabling precise cuts.
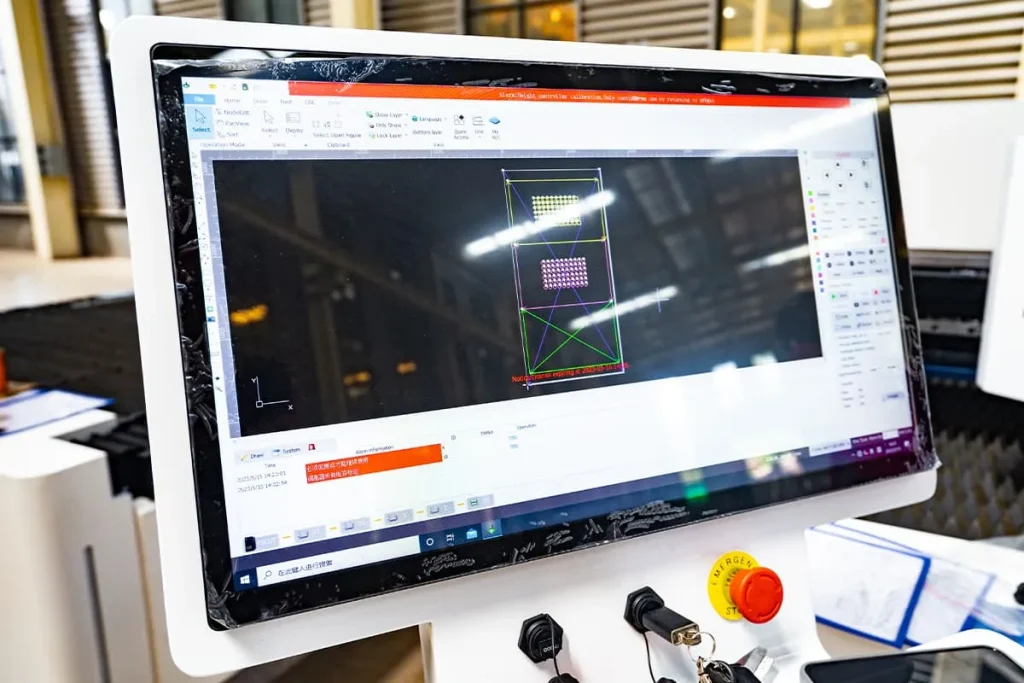
– CNC Controller: A CNC system translates design files into precise movements, guiding the cutting head and material handling mechanisms.
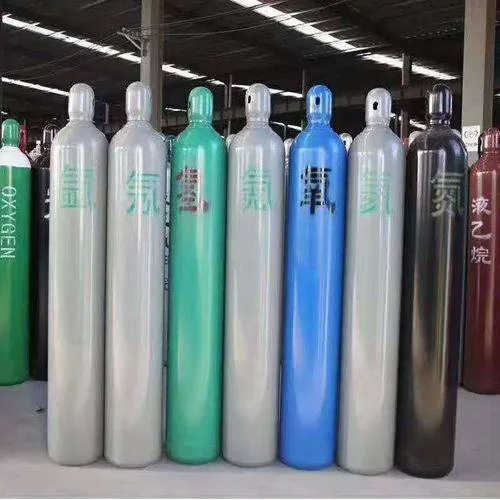
– Assist Gas System: Gases such as nitrogen or oxygen are used to assist in the cutting process, blowing away molten material and improving cut quality.
– Cooling System: This component keeps the laser source and cutting head at optimal temperatures, preventing overheating during prolonged operation.
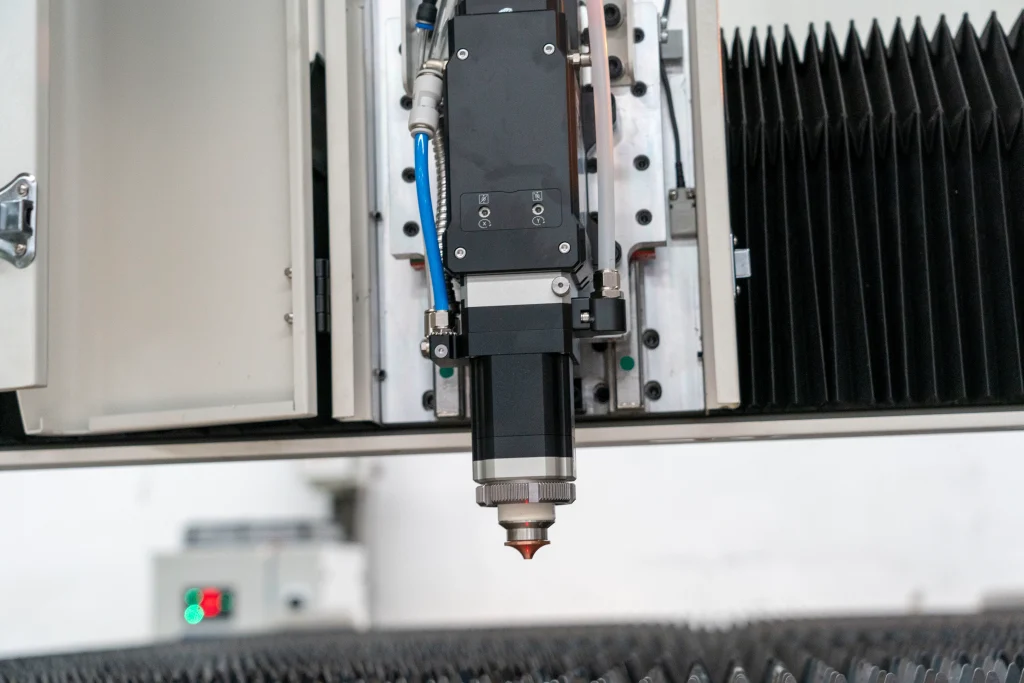




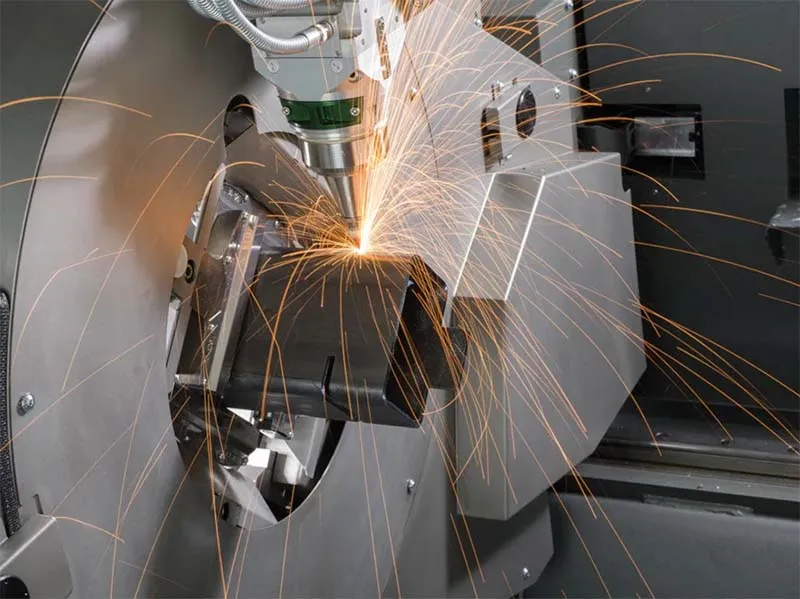
- The Laser Cutting Process Explained
1. Design Input: The cutting design is created using CAD software and then converted into a format compatible with the CNC system.
2. Material Setup: The metal sheet is placed on the cutting table and positioned accurately.
3. Laser Activation: The laser beam is focused onto the surface of the metal, creating intense heat that melts or vaporizes the material.
4. Assist Gas Application: Assist gas clears away the molten material, allowing for a clean, smooth cut.
5. Cutting Completion: Once the desired shape is achieved, the cut pieces are removed for inspection and any necessary post-processing.
3. Types of Laser Cutting Machinery: Fiber vs. CO2
Choosing the right laser cutting machinery depends on various factors, including material type, thickness, and the required level of precision. Here’s a breakdown of the two primary types of laser cutters:
Fiber laser cutting machinery is known for its high precision and efficiency. It uses a solid-state laser amplified through optical fibers, which provides several benefits:
– Smaller Beam Diameter: Allows for fine, intricate cuts, making it ideal for detailed designs.
– Effective on Reflective Metals: Fiber lasers excel in cutting metals like aluminum, brass, and copper due to their shorter wavelengths, which are better absorbed by these materials.
– Energy Efficiency: With a higher electrical efficiency, fiber lasers can reduce operating costs over time.

- CO2 Laser Cutting Machinery
CO2 laser cutting machinery uses a gas mixture, primarily CO2, to generate the laser beam. It’s often chosen for its versatility across different materials:
– Broader Beam: This makes CO2 lasers effective for cutting thicker materials, though they may lack the precision of fiber lasers for smaller details.
– Versatile Material Handling: Capable of cutting a variety of non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, and textiles.
– Lower Initial Investment: Generally, CO2 lasers have a lower upfront cost, making them accessible to businesses with budget constraints, though their maintenance requirements can be higher.
4. Advantages of Laser Cutting Machinery
Laser cutting machinery has become the preferred choice for manufacturers due to its numerous advantages. Here are the key benefits:
- Superior Precision and Tolerance
Laser cutting machinery achieves extremely tight tolerances, crucial for industries that require high precision, such as aerospace and medical devices. The ability to produce consistent and accurate parts minimizes waste and ensures perfect fits, reducing the need for adjustments during assembly.
- Enhanced Speed and Productivity
Laser cutting is significantly faster than traditional cutting methods, especially when dealing with thin metal sheets. This speed allows manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and handle large production runs with ease. By reducing cutting time, laser machinery increases overall productivity, which is particularly valuable in high-demand industries.

- Minimal Finishing Required
One of the standout benefits of laser cutting machinery is the quality of the cut edges. The laser produces smooth, burr-free edges, minimizing the need for additional finishing work such as grinding or sanding. This not only saves time but also reduces labor costs.

- Flexibility Across Various Materials
Laser cutting machinery can process a wide range of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. This versatility means manufacturers can adapt their processes to different projects without needing multiple types of equipment, making it a versatile tool in any production environment.

- Automation Capabilities
Many modern laser cutting machines come equipped with automation features such as automated material loading and unloading, real-time monitoring, and advanced CNC programming. This allows for continuous operation with minimal human intervention, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
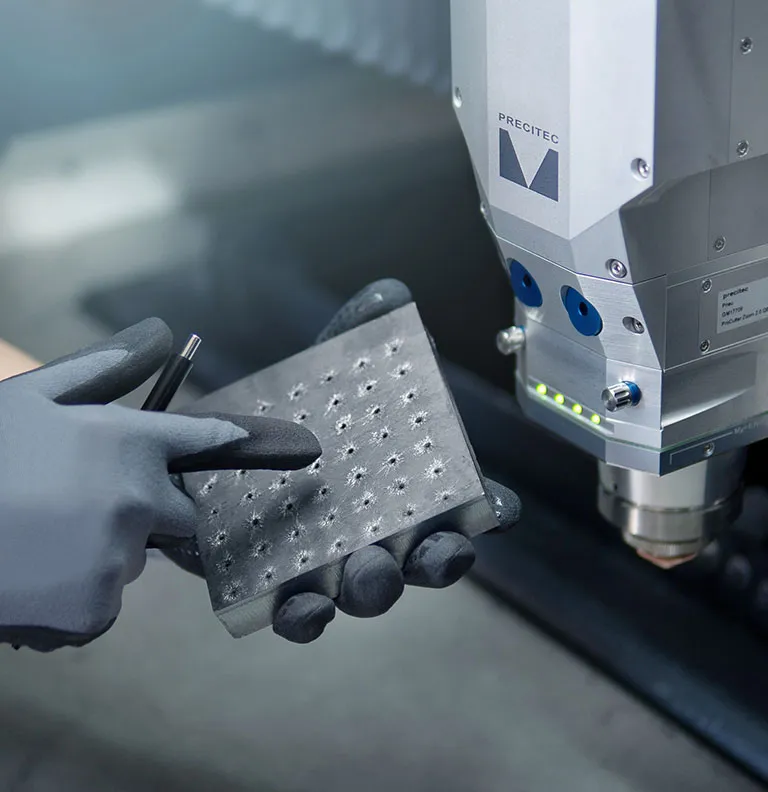

5. Applications of Laser Cutting Machinery Across Industries
Laser cutting machinery’s precision and speed have made it invaluable across various industries. Here’s how different sectors utilize this technology:
- Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, laser cutting machinery is used to produce components like body panels, engine parts, and exhaust systems. The precision offered by laser cutting ensures that each part meets the high standards required for vehicle performance and safety.

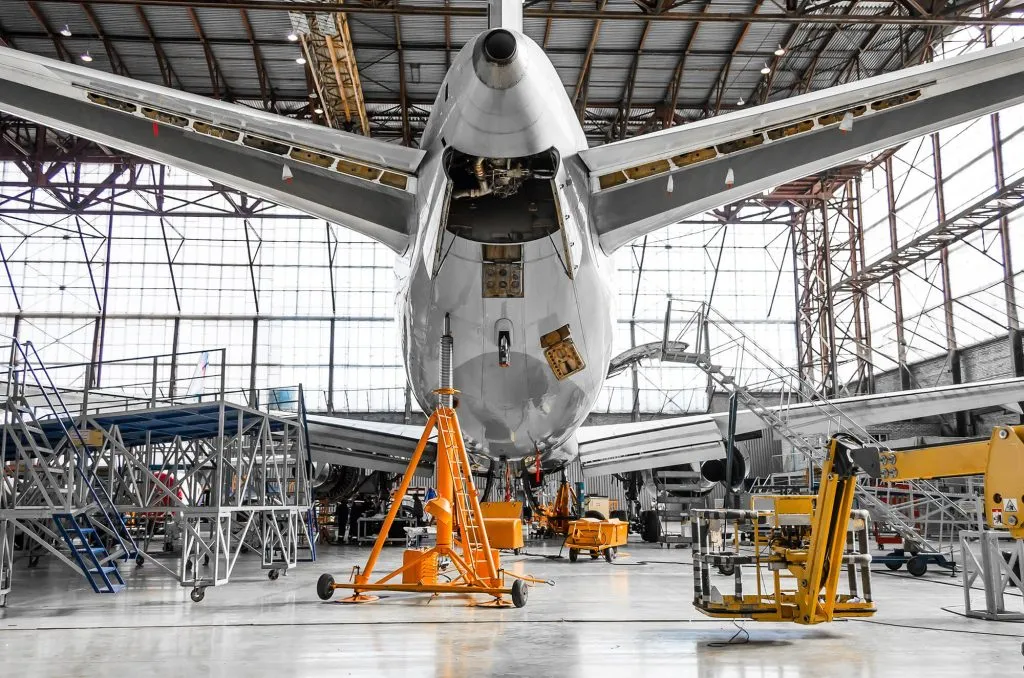
- Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace sector benefits from the ability of laser cutters to handle lightweight metals with high precision. This capability is essential for creating components that need to perform under extreme conditions, such as turbine blades and structural parts of aircraft.

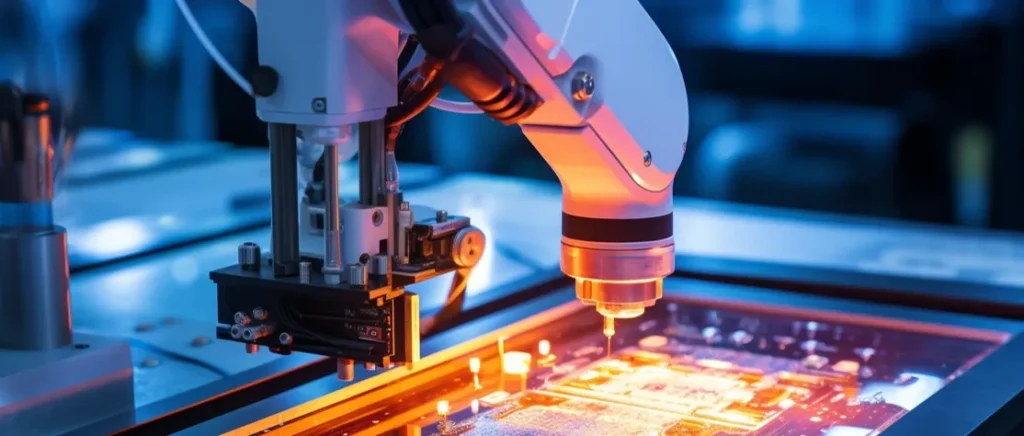
- Electronics and Microelectronics
For the production of electronic devices, laser cutting is used to manufacture heat sinks, enclosures, and intricate metal parts. The ability to produce precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones ensures that sensitive electronic components remain undamaged.

- Architectural Design
In architecture, laser cutting enables the creation of intricate metal facades, railings, and structural elements. The technology allows architects to bring complex designs to life, providing a blend of strength and aesthetic appeal for modern buildings.

- Medical Equipment
Laser cutting machinery plays a critical role in manufacturing surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic devices. The precision and cleanliness of laser cuts are crucial in maintaining the sterility and functionality of medical instruments.
6. Choosing the Right Laser Cutting Machinery: Key Considerations
Selecting the most suitable laser cutting machinery involves careful consideration of several factors:
- Material Compatibility and Thickness
Different materials require different power levels for optimal cutting. Fiber lasers are more efficient for thin metals and reflective materials, while CO2 lasers may be more suitable for thicker metals and mixed-material projects.

- Balance Between Speed and Detail
If your projects require detailed cuts, a fiber laser with high precision capabilities may be the best choice. However, for thicker materials where speed is a priority, a CO2 laser could be more efficient. Testing the machine’s capabilities with sample materials can provide insight into which option will best meet your needs.
- Long-Term Costs
While initial purchase price is important, it’s also crucial to consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, power consumption, and the availability of replacement parts. Fiber lasers typically have lower maintenance requirements, making them a good option for reducing long-term operational expenses.

- Integration and Automation
For manufacturers aiming for high-volume production, look for laser cutting machinery that supports automation. Features like automatic material feeders and real-time adjustment capabilities can significantly enhance production efficiency, allowing for 24/7 operations without manual intervention.

7. Optimizing Laser Cutting Machinery for Maximum Efficiency
To get the best results from laser cutting machinery, manufacturers must fine-tune their settings to match the specific requirements of each project:
- Power Settings and Material Thickness
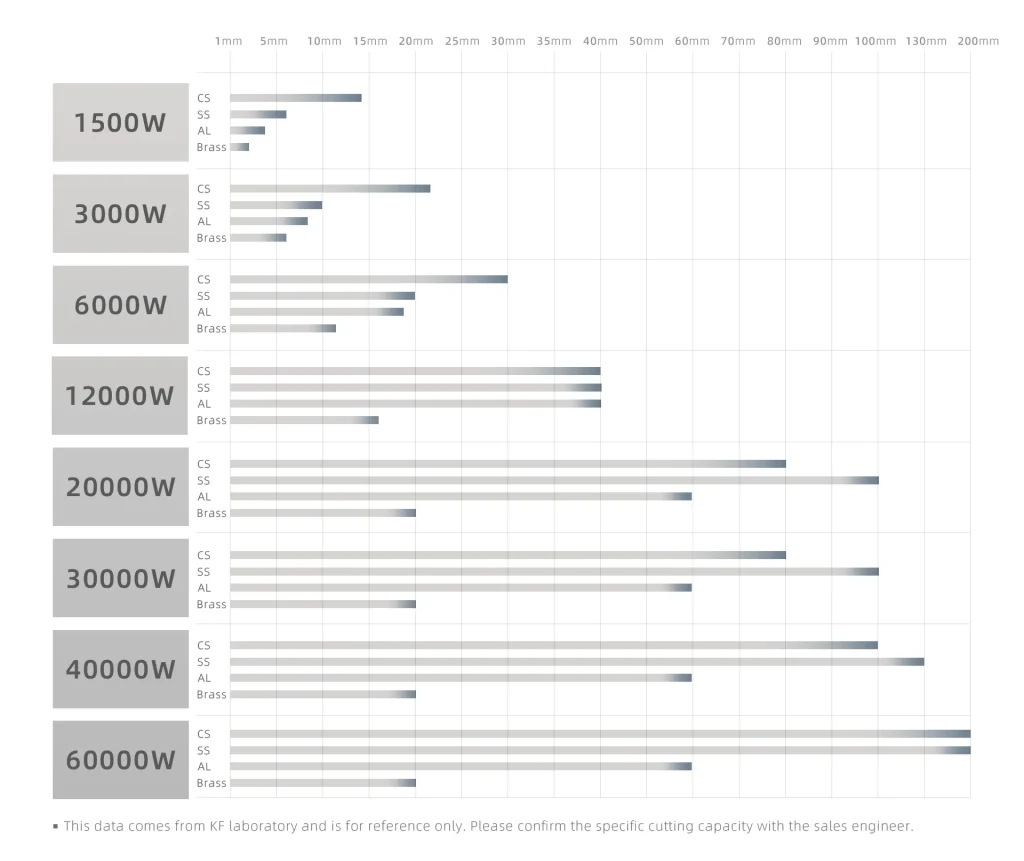
Adjusting the laser power based on the thickness of the metal ensures efficient cutting without damaging the material. For thicker sheets, higher power is necessary, while thinner sheets require lower power to prevent burning.
- Focus Adjustments
Proper focus ensures that the laser beam is concentrated on the desired spot, resulting in precise cuts. Regularly calibrating the focus settings can help maintain the quality of cuts, especially when switching between different materials.

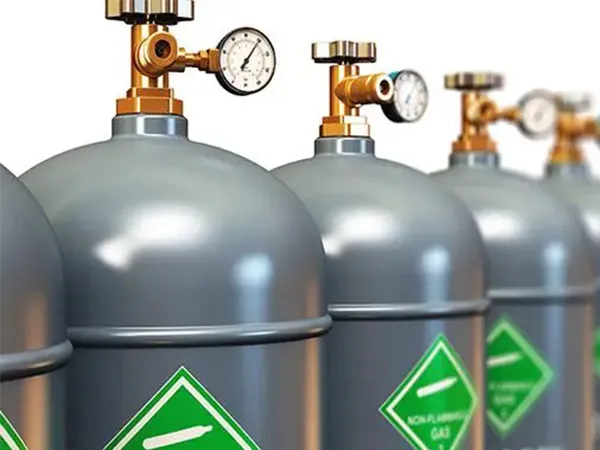
- Gas Selection
Choosing the right assist gas, such as nitrogen for cleaner cuts or oxygen for faster cutting speeds, can significantly impact the quality of the cut and the speed of production. Understanding how each gas interacts with different metals can help optimize the cutting process.

8. Trends Shaping the Future of Laser Cutting Machinery
As technology advances, laser cutting machinery is becoming more sophisticated, offering improved capabilities and greater efficiency. Key trends to watch include:
– Hybrid Technology: Machines that combine fiber and CO2 capabilities, providing a versatile solution for manufacturers working with varied materials.
– AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI for real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance helps in optimizing cutting paths, improving accuracy, and reducing machine downtime.
– Environmentally Friendly Innovations: As industries become more conscious of their carbon footprint, energy-efficient laser cutters that use less power while delivering high-quality results are becoming more popular.
These trends ensure that laser cutting machinery will continue to evolve, offering enhanced capabilities for manufacturers seeking to stay competitive.

Final Takeaways
Laser cutting machinery represents a vital tool in modern production, offering unmatched precision, speed, and adaptability. By selecting the right machine and fine-tuning its operation, manufacturers can achieve significant efficiency gains, producing high-quality parts across diverse industries. Understanding the strengths of each type of laser cutting machinery and keeping up with emerging trends ensures that your production line remains at the forefront of technology.
Top Stories
-
 Unleashing the Power of Tube Laser Cutting Machines: A Comprehensive Guide07 Mar 2026
Unleashing the Power of Tube Laser Cutting Machines: A Comprehensive Guide07 Mar 2026 -
 How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter for Sale: A Buyer’s Complete Guide03 Mar 2026
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter for Sale: A Buyer’s Complete Guide03 Mar 2026 -
 CNC Laser for Metal | Precision Cutting28 Feb 2026
CNC Laser for Metal | Precision Cutting28 Feb 2026 -
 CNC Laser Tube Cutting Machine | Precision Machines for Sale24 Feb 2026
CNC Laser Tube Cutting Machine | Precision Machines for Sale24 Feb 2026 -
 4KW Fiber Laser Cutting Machine | Industrial Guide20 Feb 2026
4KW Fiber Laser Cutting Machine | Industrial Guide20 Feb 2026
Product Categories
- Metal Laser Cutter
- Laser Welder Machine
- Laser Cleaner Machine
- Laser Marker Machine
- Press Brake Machine