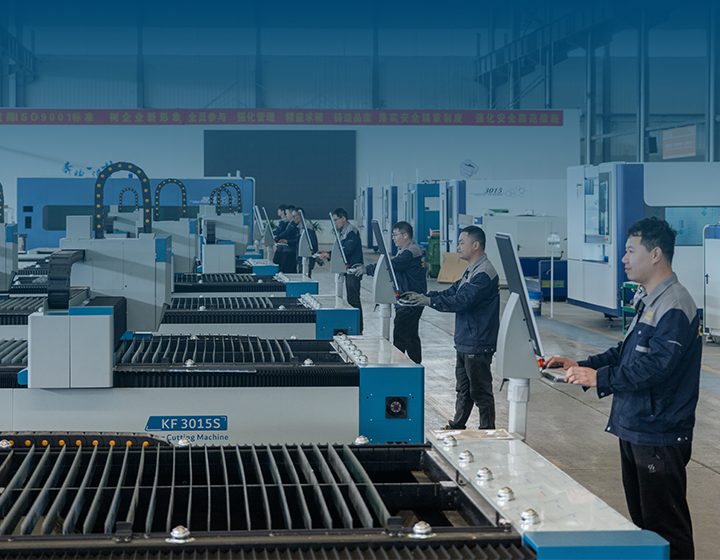
Noticias
Guía completa de máquinas de corte láser para fabricación de metales
1. Introducción a las máquinas láser cortadas
Las máquinas láser cortadas han revolucionado la industria manufacturera, especialmente en el campo de la fabricación de metales. Utilizando vigas láser altamente enfocadas, Estas máquinas pueden crear cortes precisos, grabados, y diseños intrincados en una variedad de superficies metálicas. A diferencia de los métodos de corte tradicionales, Cortar las máquinas láser funcionan con extrema precisión y eficiencia, Hacerlos herramientas indispensables para industrias que van desde el automóvil hasta el aeroespacial. En esta guía, Exploraremos los diferentes tipos de máquinas láser cortadas., sus principios de trabajo, ventajas, Desafíos comunes, y aplicaciones en varias industrias.
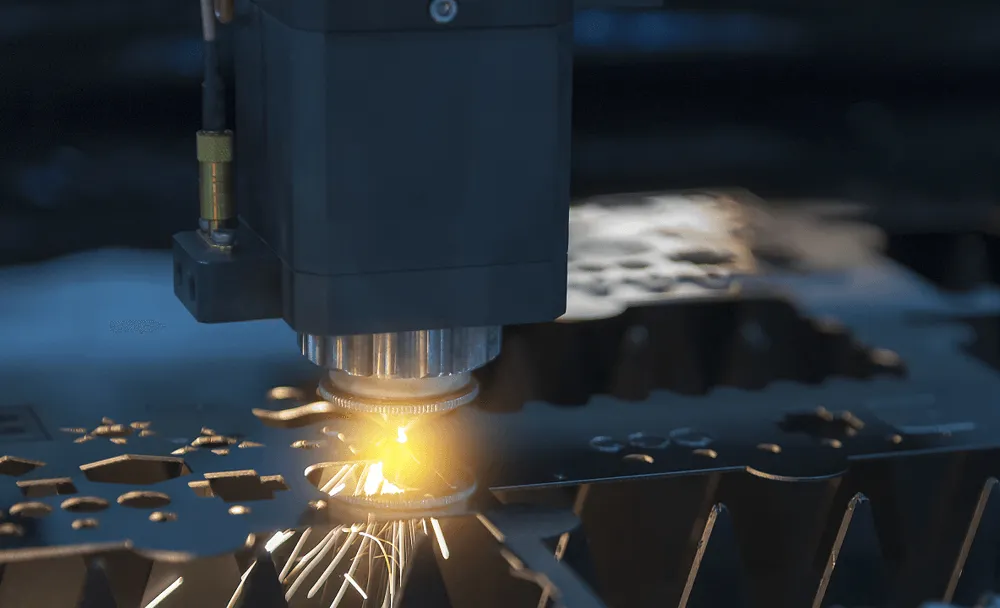

2. ¿Qué es un Cortar máquina láser?
Una máquina láser cortada es una herramienta de alta precisión que utiliza un rayo láser concentrado para cortar, grabar, o marcar materiales, particularmente metales. El proceso implica dirigir un haz láser de alta energía sobre la superficie de un material, fusión, incendio, o vaporizarlo para crear un corte. La ruta del láser se controla con precisión por el control numérico de la computadora (CNC) tecnología, Permitir formas y diseños intrincados que serían difíciles o imposibles de lograr con métodos manuales.

- Cómo funciona una máquina láser cortada
Cortar las máquinas láser operan utilizando algunos pasos fundamentales:
– Generación de haz láser: El láser se genera utilizando varios medios como el gas CO2, fibra óptica, o materiales de cristal. Este haz se dirige a través de una serie de espejos o fibra óptica para enfocarlo.
– Enfocando el láser: El haz se concentra a través de una lente hasta un punto preciso, Creación de un área de alta intensidad capaz de cortar metales.
– Interacción material: A medida que el haz enfocado interactúa con la superficie del metal, Calienta el área a un punto donde se derrite o vaporiza. El corte se logra a medida que el material se retira de la zona calentada..
– Uso de gases de asistencia: Gases como el nitrógeno, oxígeno, o el argón a menudo se usan para eliminar el material fundido del área de corte, Asegurar bordes limpios y precisos.
3. Tipos de máquinas láser cortadas
Las máquinas láser cortadas se clasifican en función de la tecnología utilizada para generar el rayo láser. Cada tipo tiene fortalezas específicas que lo hacen adecuado para diferentes aplicaciones.
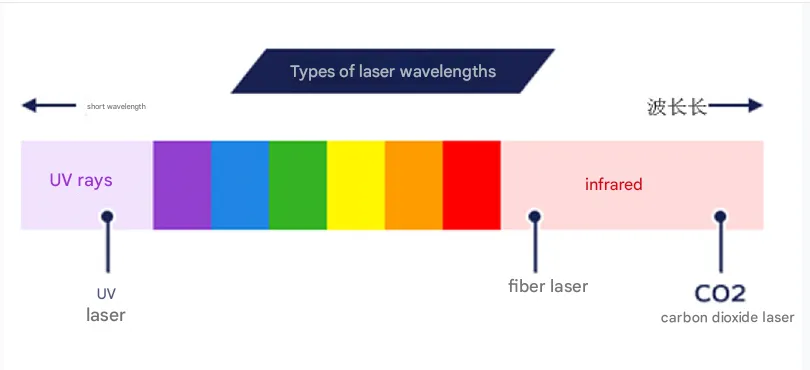
- Máquinas láser de CO2
Las máquinas láser de CO2 usan una mezcla de gas que incluye dióxido de carbono, nitrógeno, y helio para producir un haz láser. Son particularmente efectivos para cortar materiales no metálicos como la madera, acrílico, y cuero pero también puede manejar ciertos metales, Hojas especialmente delgadas de aluminio y acero suave.
– Ventajas:
– Adecuado para una amplia gama de materiales más allá de los metales.
– Capaz de lograr bordes suaves y pulidos en materiales como acrílico.
– Desafíos:
– Requiere más mantenimiento debido a la necesidad de recargas de gas y sistemas de enfriamiento regulares.
– Lucha con cortar metales altamente reflectantes como el cobre.

Las máquinas láser de fibra son parte del grupo láser de estado sólido. Utilizan cables de fibra óptica infundidos con elementos de tierra rara para generar y amplificar el haz láser. Los láseres de fibra son ideales para cortar metales como el acero inoxidable, latón, y aluminio.
– Ventajas:
– Alta eficiencia y mantenimiento mínimo en comparación con los láseres a base de gas.
– Excelente para cortar metales reflectantes, Gracias a su longitud de onda más corta.
– Vida operativa larga, a menudo excediendo 25,000 horas.
– Desafíos:
– Inversión inicial más alta, Aunque los costos operativos más bajos compensan esto con el tiempo.
– El más adecuado para las hojas de metal más delgadas, con materiales más gruesos que requieren una mayor potencia de salida.

- Dakota del Norte:YAG y Nd:Láseres de cristal yvo
Estos láseres usan medios de cristal como el granate de aluminio de Yttrium dopado con neodimio (Dakota del Norte:YAG) o Yttrium orto-anhanadate (Dakota del Norte:Yvo) para producir el rayo láser. Ofrecen densidades de poder muy altas, Hacerlos adecuados para aplicaciones que requieren cortes profundos y grabado preciso.
– Ventajas:
– Alta precisión adecuada para grabado y marcado detallados.
– Efectivo para una variedad de metales y ciertas cerámicas.
– Desafíos:
– Vida más corta del medio láser en comparación con los láseres de fibra.
– Mayores costos de mantenimiento debido a la necesidad de reemplazar diodos de bomba.
4. Beneficios del uso de máquinas láser cortadas
Las máquinas láser cortadas han ganado popularidad debido a sus numerosas ventajas sobre los métodos de corte tradicionales. He aquí por qué se prefieren en metalurqueo:
- Precisión superior
La capacidad de producir cortes con tolerancias tan bajas como +/- 0.01 MM hace que las máquinas láser sean ideales para aplicaciones donde la precisión es crítica, como componentes aeroespaciales o dispositivos médicos.
- Procesamiento de alta velocidad
Las máquinas láser cortadas pueden funcionar a altas velocidades, haciéndolos perfectos para la producción en masa. Su capacidad para cortar los materiales rápidamente sin comprometer la calidad mejora la eficiencia de fabricación general..
- Bordes limpios y suaves
El rayo láser enfocado asegura que la zona afectada por el calor (Cría) es mínimo, conduciendo a bordes limpios que a menudo requieren poco o ningún postprocesamiento. Esta característica reduce el tiempo y el costo asociados con el trabajo de acabado..
- Versatilidad del material
El corte láser es adecuado para una variedad de metales, incluyendo acero inoxidable, acero suave, aluminio, y aleaciones. Esta versatilidad lo convierte en una solución ideal para los fabricantes que se ocupan de diferentes tipos de materiales..
- Desechos reducidos
La precisión del corte por láser minimiza el desperdicio de material, Como el ancho de kerf estrecho asegura que solo se elimine el material necesario. Esto no sólo reduce los costes sino que también hace que el proceso sea más respetuoso con el medio ambiente..
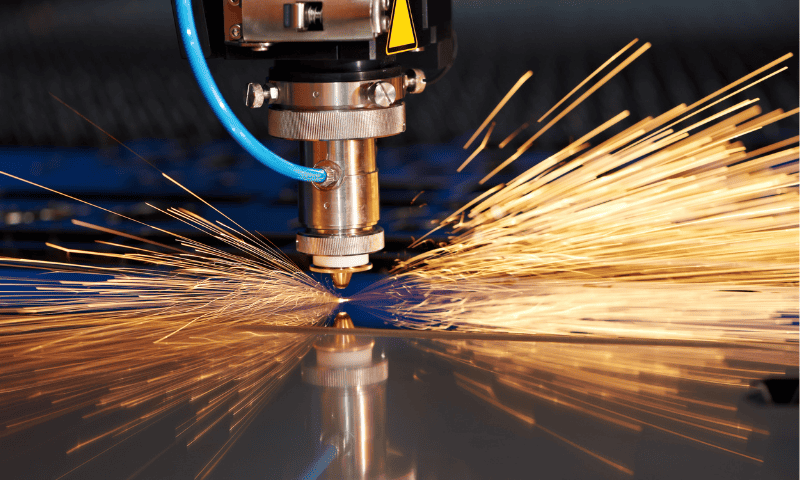



5. Factores clave a considerar al elegir una máquina láser cortada
Seleccionar la máquina láser de corte correcto requiere una comprensión de varios factores para garantizar un rendimiento óptimo y rentabilidad.
- Tipo de material y espesor
El tipo de material y su grosor influyen directamente en la elección del láser. Por ejemplo, Los láseres de fibra son mejores para cortar metales reflectantes como el aluminio, mientras que los láseres de CO2 son adecuados para materiales no metálicos. Los materiales más gruesos pueden requerir láseres con mayor potencia de salida para lograr cortes limpios.

- Potencia y velocidad láser
La calificación de potencia de un láser afecta la velocidad y la profundidad de la corte. Una mayor potencia permite un corte más rápido y la capacidad de cortar materiales más gruesos, pero también aumenta el consumo de energía. Equilibrar la potencia con los requisitos de material garantiza un funcionamiento eficiente.

- Tamaño del área de trabajo
El tamaño del área de trabajo del láser determina el tamaño máximo de las sábanas o placas que se pueden procesar. Para industrias que se ocupan de grandes partes, Una máquina con una cama de trabajo más grande es esencial.
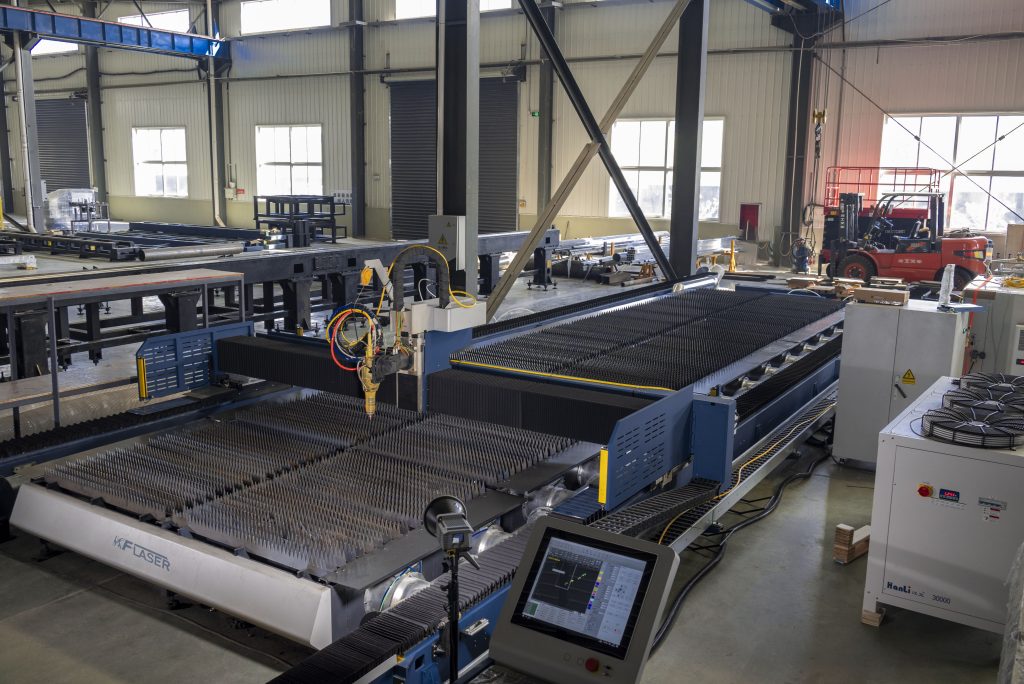

- Necesidades de mantenimiento
Mientras que los láseres de fibra requieren menos mantenimiento, Los láseres de CO2 necesitan controles regulares de los niveles de gas y espejos. Comprender los requisitos de mantenimiento puede ayudar en el presupuesto y garantizar que la máquina funcione sin problemas.

6. Desafíos comunes en el corte con láser y las soluciones
Mientras que las máquinas láser cortadas ofrecen muchas ventajas, Pueden surgir ciertos desafíos durante la operación. Aquí le mostramos cómo abordar algunos de los problemas comunes.:
- Gestión de la distorsión del calor
Cortar materiales gruesos o sensibles al calor puede conducir a deformación. El uso de gases de asistencia como nitrógeno o ajuste de la velocidad de corte puede ayudar a administrar la distribución de calor., reduciendo el riesgo de distorsión.

- Lidiar con metales reflexivos
Cortar metales como cobre y latón puede ser un desafío debido a sus propiedades reflexivas, que puede causar la reflexión de retroceso láser. Láser de fibra, con su longitud de onda más corta, son más efectivos para manejar estos materiales.
- Formación de rebabas
Las rebabas pueden formarse cuando el enfoque del láser no se establece correctamente o cuando la velocidad de corte es demasiado alta. La calibración regular de la cabeza del láser y el ajuste de la configuración de potencia pueden reducir la aparición de rebabas.

7. Aplicaciones de máquinas láser cortadas en diversas industrias
La adaptabilidad de las máquinas láser cortadas los convierte en un activo valioso en una variedad de industrias. Estos son algunos de los sectores clave que se benefician de esta tecnología.:
- Industria automotriz
En el sector del automóvil, El corte con láser se usa para fabricar paneles de cuerpo, Creación de componentes intrincados del motor, y cortar materiales livianos para interiores de vehículos. La precisión de las máquinas láser garantiza un ajuste perfecto para las piezas, que es crucial para la seguridad y el rendimiento del vehículo.

- Sector aeroespacial
El corte láser es esencial en la fabricación aeroespacial para crear componentes a partir de aleaciones de alta resistencia. La capacidad de mantener tolerancias estrictas es vital en esta industria, donde incluso las desviaciones menores pueden tener impactos significativos en la seguridad y el rendimiento.

- Electrónica y bienes de consumo
Para la industria electrónica, Las máquinas láser cortadas se utilizan para crear recintos, marcos, y complejas placas de circuito. La precisión y la capacidad de cortar pequeños, Los diseños detallados hacen que los láseres sean ideales para estas aplicaciones.

- Fabricación de dispositivos médicos
En producción de dispositivos médicos, El corte láser se utiliza para fabricar herramientas quirúrgicas, implantes, y dispositivos médicos complejos. La naturaleza sin contacto del proceso garantiza que no haya contaminación., un factor crítico en esta industria.
8. Consejos para optimizar el rendimiento de una máquina láser cortada
Maximizar la eficiencia y la vida útil de una máquina láser cortada requiere atención a los detalles y un mantenimiento adecuado.
- Limpieza de rutina de óptica
La óptica, incluyendo lentes y espejos, debe limpiarse regularmente para garantizar que el haz láser permanezca enfocado y potente. La óptica sucia puede dispersar el haz, conduciendo a cortes inconsistentes.

- Configuración de enfoque correcto
Asegurarse de que el láser se centre adecuadamente en la superficie del material es fundamental para lograr cortes limpios. Muchas máquinas vienen con sistemas de enfoque automático, Pero los ajustes manuales aún pueden ser necesarios para resultados óptimos.
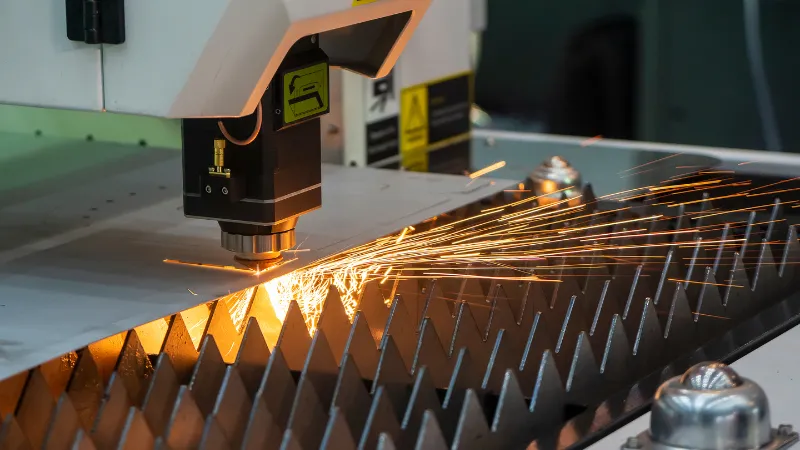

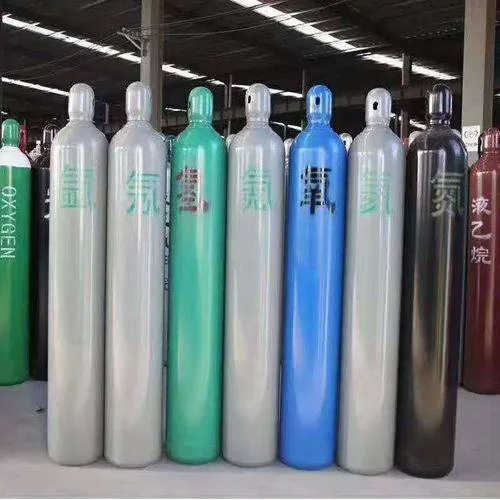
- Uso de gas de asistencia de calidad
Uso de gas de alta pureza, como oxígeno o nitrógeno, puede mejorar la calidad y la velocidad de la vanguardia. La elección correcta de gas depende del material que se corta y el acabado deseado.

- Calibración periódica
La calibración de la máquina láser garantiza regularmente que el movimiento de la cabeza del láser coincida con la ruta programada con precisión. Esto evita las desviaciones en los recortes, especialmente para formas complejas.

9. Tendencias futuras en la tecnología de corte con láser
A medida que avanza la tecnología, Las máquinas láser cortadas se están volviendo más sofisticadas, con características que mejoran la precisión, eficiencia, y facilidad de uso. Las tendencias como la integración de IA para el ajuste automático de los parámetros de corte y las mejoras en la potencia del láser de fibra están dando forma al futuro del corte láser.
– Automatización y IA: Los sistemas automatizados y la IA se están integrando en máquinas láser para un mejor control sobre los procesos de corte, Reducir el error humano.
– Soluciones ecológicas: Los esfuerzos para reducir el consumo de energía e integrar tecnologías más ecológicas están llevando a prácticas de corte con láser más sostenibles.
– Compatibilidad de material avanzado: Se están realizando avances continuos para expandir la gama de materiales que se pueden cortar eficientemente, incluyendo compuestos y aleaciones avanzadas.



Abrazando el potencial del corte láser
Las máquinas láser cortadas han cambiado el paisaje de la fabricación al ofrecer precisión y eficiencia inigualables. Su versatilidad los hace adecuados para varias industrias, Desde complejos electrónicos hasta piezas automotrices robustas. A medida que la tecnología continúa avanzando, Estas máquinas permanecerán a la vanguardia de la innovación., proporcionando la precisión y velocidad que exige la fabricación moderna. Adoptar el poder de la tecnología de corte con láser no se trata solo de lograr cortes más limpios, se trata de superar los límites de lo que es posible en el mundo de la fabricación de metales..
Historias destacadas
-
 Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machine For Sale05 Dic 2025
Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machine For Sale05 Dic 2025 -
 4000 Láser de vatios | Poder de corte industrial02 Dic 2025
4000 Láser de vatios | Poder de corte industrial02 Dic 2025 -
 6 corte por láser kw | guía de precisión industrial28 Nov 2025
6 corte por láser kw | guía de precisión industrial28 Nov 2025 -
 Revolucionando la industria con la máquina cortadora láser de tubos de acero25 Nov 2025
Revolucionando la industria con la máquina cortadora láser de tubos de acero25 Nov 2025 -
 10Corte por láser en kW | Precisión & Fuerza21 Nov 2025
10Corte por láser en kW | Precisión & Fuerza21 Nov 2025
Categorías de productos
- Cortador láser de metales
- Máquina soldadora láser
- Máquina limpiadora láser
- Máquina marcadora láser
- Prensa plegadora




